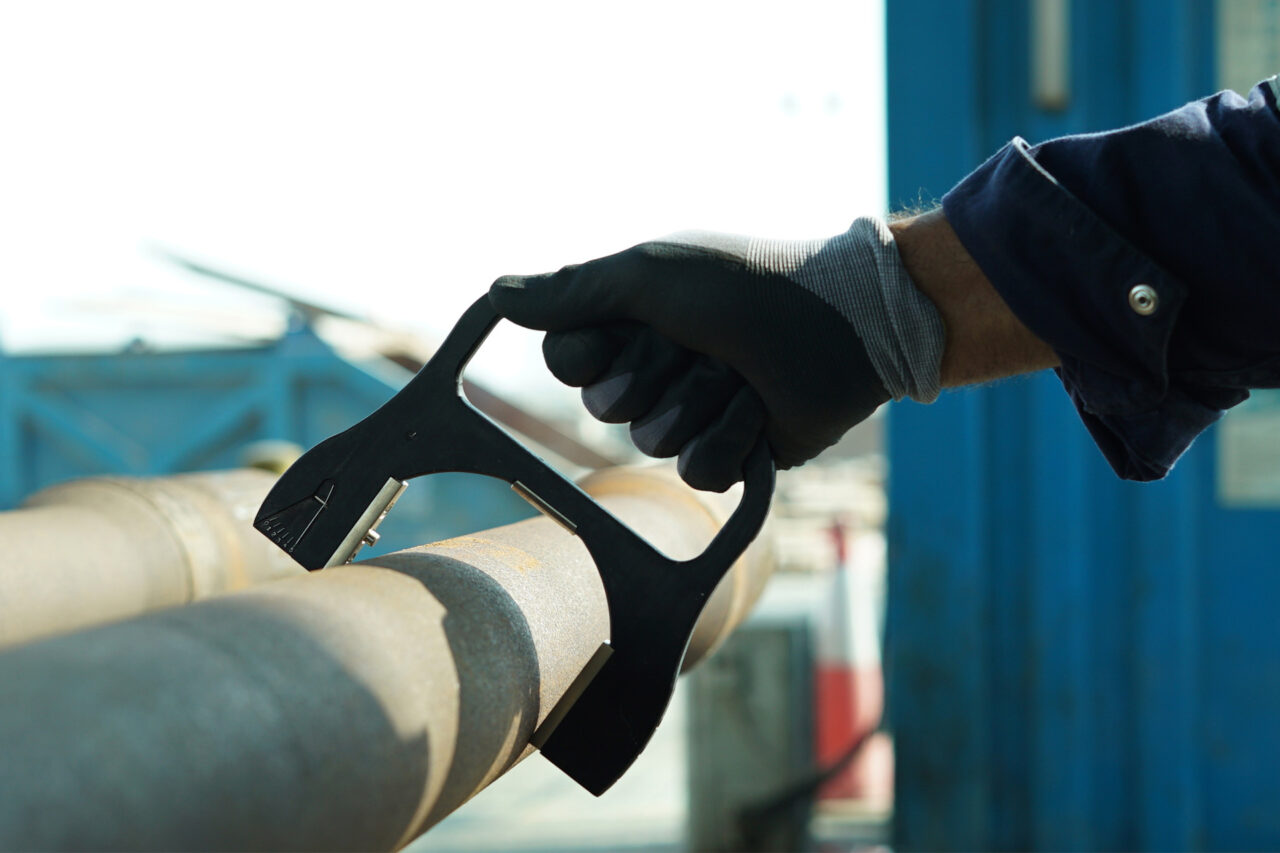
Inspections or Testing are quite common in various industry sectors including Oil and Gas, Construction, Automotive, Aerospace, Mining, Fabrication, Rail and Power Generation. But some technology used in such processes tends to cause damage to the parts or materials that are being tested. Now, new cutting-edge techniques are implemented by industries to eliminate such risks, thanks to the evolution of technology. This includes Non-Destructive Testing.
What is Non-Destructive Testing?
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a crucial technique used in engineering, manufacturing, and construction to assess the properties of materials, components, or systems without causing any damage or alteration. By employing NDT, industries can safely inspect and evaluate materials, identify defects, flaws, or potential risks, and ensure the reliability and safety of their products.
Let’s delve into the world of NDT by exploring its key aspects:
1. Visual Testing (VT):
- Method: Inspection using the naked eye or optical aids.
- Purpose: Detect surface defects, irregularities, and visual anomalies.
- Application: Commonly used for weld inspections, corrosion assessment, and general visual examination.
2. Particle Testing (MT):
- Method: Magnetizing the material and applying magnetic particles to reveal surface or near-surface defects.
- Purpose: Detect cracks, seams, and other discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials.
- Application: Used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
3. Penetrant Testing (PT):
- Method: Applying a liquid penetrant to the surface, followed by developer to reveal defects.
- Purpose: Detect surface-breaking defects such as cracks and porosity.
- Application: Widely used in aerospace, automotive, and metalworking industries.
4. Ultrasonic Testing (UT):
- Method: Sending high-frequency sound waves into the material and analyzing the reflected waves.
- Purpose: Detect internal flaws, thickness measurements, and material characterization.
- Application: Used for weld inspections, structural assessments, and flaw detection.
5. Radiographic Testing (RT) and Digital Radioscopy (DR):
- Method: X-rays or gamma rays penetrate the material, creating an image on film or digital detectors.
- Purpose: Reveal internal defects, voids, and structural irregularities.
- Application: Commonly employed in the aerospace, nuclear, and petrochemical industries.
Are you looking for expert Non-Destructive Testing?
At Tubecare, we are committed to offering high-quality services in Non-Destructive Inspections to help support Oil & Gas industries in the best possible way. Get in touch and get started now.